
Your phone buzzes at 3 AM. You grab it without thinking. Sound familiar? You're not alone—210 million people worldwide are stuck in this exact cycle right now.
Social Media Addiction Statistics reveal something most won't admit: we're hooked.
From teenagers spending 7+ hours daily scrolling to adults checking feeds before even getting out of bed, the numbers paint a concerning picture.
But here's what nobody tells you about the real cost of those endless scrolls, likes, and notifications consuming your life.
Global Prevalence of Social Media Addiction
The scope of social media addiction extends far beyond casual overuse, representing a genuine behavioral addiction that affects millions worldwide.
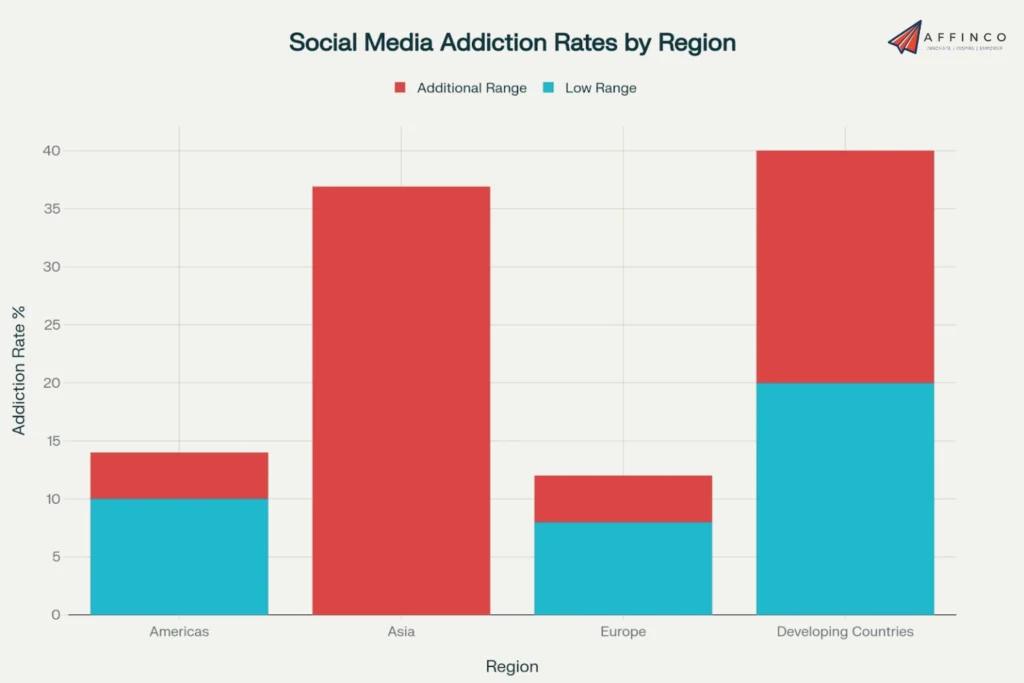
Key Global Statistics:
The dopamine-driven design of modern social media platforms has created what researchers term “digital slot machines,” where users receive intermittent rewards through likes, comments, and shares, reinforcing compulsive behavior patterns.
Demographic Snapshot of Social Media Addiction
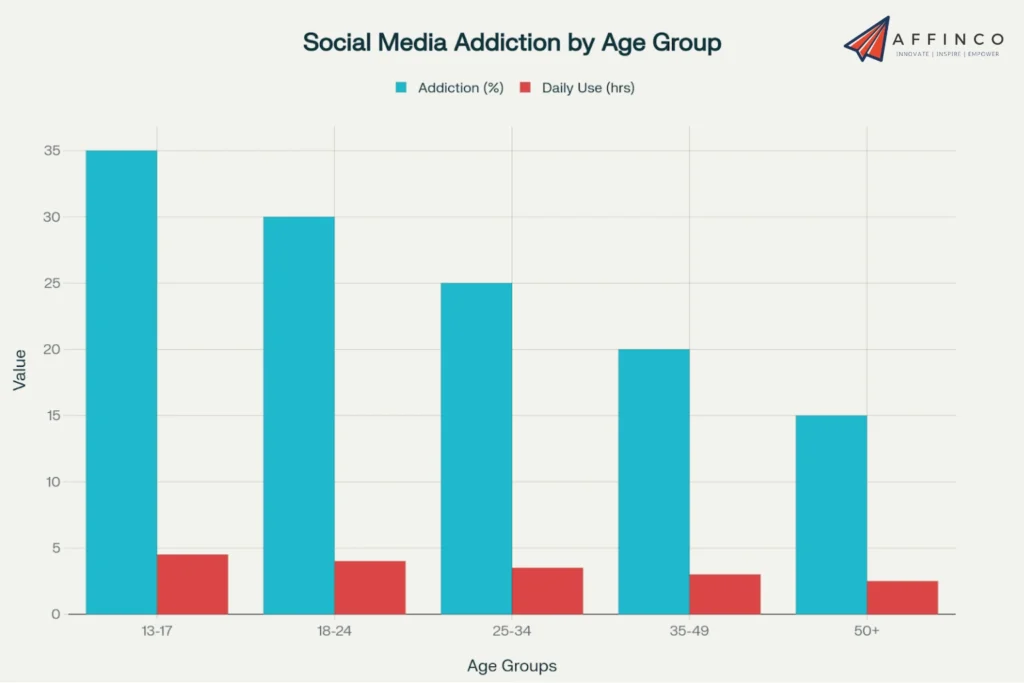
Understanding who is most affected by social media dependency helps identify at-risk populations and inform targeted intervention strategies.
Age Demographics
Teenagers and young adults remain the most vulnerable population to social media addiction, with usage patterns showing concerning trends across age groups.
| Age Group | Addiction Prevalence | Average Daily Usage | Most Affected Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13-17 years | 70% | 7.2 hours | TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat |
| 18-24 years | 65% | 6.8 hours | TikTok, Instagram, Twitter |
| 25-34 years | 45% | 4.5 hours | Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn |
| 35-49 years | 32% | 3.2 hours | Facebook, LinkedIn, YouTube |
| 50+ years | 18% | 2.1 hours | Facebook, YouTube |
Detailed Age-Related Findings:
Gender and Social Media Addiction
Research reveals interesting patterns in how gender influences social media addiction and related behaviors.
Gender-Specific Statistics:
Platform-Specific Addiction Rates and Usage Patterns
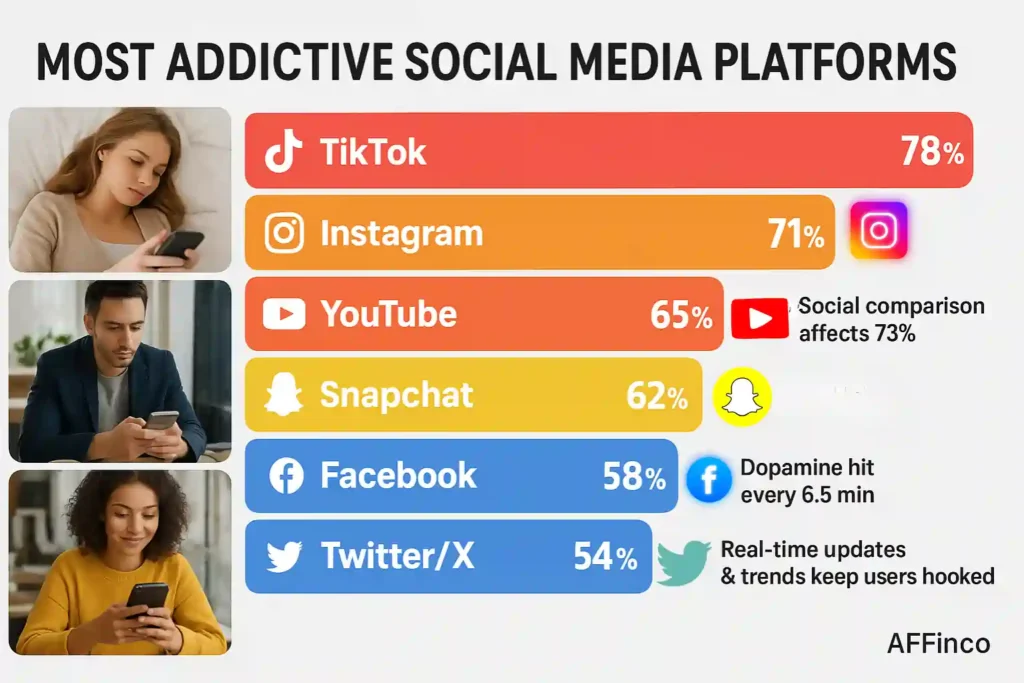
Different social media platforms employ varying engagement strategies that contribute to addictive behaviors. Understanding platform-specific addiction rates helps identify the most problematic digital environments.
Most Addictive Social Media Platforms
Current data shows significant variation in addiction potential across different platforms, largely influenced by their design features and content delivery mechanisms.
| Platform | Monthly Usage Hours | Addiction Rate | Key Addictive Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| TikTok | 34.1 hours | 78% | Infinite scroll, short videos, algorithm |
| YouTube | 28.3 hours | 65% | Autoplay, recommendations, long content |
| 26.7 hours | 71% | Stories, reels, visual content, likes | |
| 22.4 hours | 58% | News feed, notifications, social validation | |
| Snapchat | 21.8 hours | 62% | Streaks, disappearing content, FOMO |
| Twitter/X | 19.2 hours | 54% | Real-time updates, trending topics |
Platform-Specific Insights:
Daily Usage Patterns and Screen Time
Excessive screen time represents a core component of social media addiction, with usage patterns showing alarming increases across all demographics.
Daily Usage Statistics:
Compulsive Checking Behaviors:
Psychological and Mental Health Impact
Social media addiction creates significant mental health consequences that extend far beyond simple time wastage. The psychological effects represent one of the most concerning aspects of digital dependency.
The relationship between excessive social media use and mental health deterioration has been extensively documented, with multiple studies showing causal links between platform engagement and psychological distress.
Core Mental Health Statistics
Social media users are 3.1 times more likely to experience clinical depression.
Anxiety and Depression Correlations
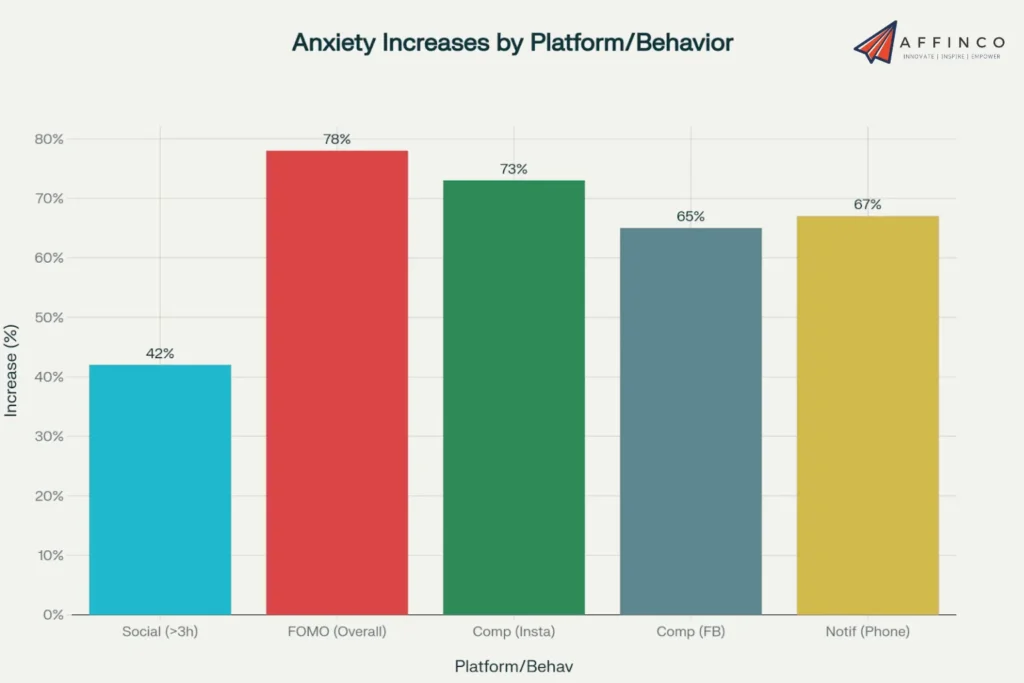
Social media-induced anxiety manifests through various mechanisms, including social comparison, fear of missing out, and validation-seeking behaviors.
Anxiety-Related Findings:
- Social anxiety increases by 42% in users who spend more than 3 hours daily on social platforms.
- FOMO affects 78% of social media users, with millennials and Gen Z showing highest rates.
- Comparison-based anxiety occurs in 73% of Instagram users and 65% of Facebook users.
- Notification anxiety affects 67% of smartphone users, creating stress when separated from devices.
Depression and Social Isolation:
- Passive social media consumption (scrolling without engagement) increases depression risk by 87%.
- Social isolation paradox: Despite increased connectivity, 32% of heavy users report feeling more alone.
- Cyberbullying increases depression rates by 70% among affected teenagers.
- Sleep disruption from social media use contributes to depression in 64% of cases.
Self-Esteem and Body Image Issues
Social media platforms significantly impact self-perception and body image, particularly among younger users exposed to idealized content.
Self-Esteem affected by Social Media Addiction
Physical Health Consequences
Beyond psychological effects, social media addiction creates numerous physical health problems that impact overall well-being and quality of life.
Sleep Disruption and Circadian Rhythm
Blue light exposure from screens interferes with natural circadian rhythms, while the dopamine stimulation from social media creates alertness that prevents proper sleep preparation.
Posture and Musculoskeletal Problems
Extended periods of device usage create various musculoskeletal issues that can become chronic without intervention.
Economic and Social Impact

Social media addiction creates broader societal consequences that extend beyond individual health, affecting productivity, relationships, and economic output.
Understanding the macro-level effects of digital dependency helps quantify the true cost of social media addiction to society and the global economy.
Workplace Productivity Impact:
Relationship and Social Consequences
Digital relationships often replace face-to-face interactions, leading to deterioration in social skills and meaningful connections.
- 45% of couples report social media negatively affecting their relationship quality.
- Social skills deterioration occurs in 58% of heavy users, particularly affecting in-person communication.
- Family meal disruption: 73% of families report devices interfering with meal conversation.
- Friendship quality decline affects 41% of individuals prioritizing online over offline relationships.
Educational and Academic Performance
Student populations show particular vulnerability to academic performance decline related to social media addiction.
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Social Media Addiction
Recognizing addiction symptoms enables early intervention and treatment before dependency behaviors become entrenched.
Behavioral addiction symptoms mirror those of substance addiction, including tolerance, withdrawal, and continued use despite negative consequences.
Primary Warning Signs:
Clinical Assessment Criteria:
- Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale identifies addiction in 23% of regular users.
- Diagnostic criteria fulfillment: 18% of heavy users meet clinical addiction thresholds.
- Co-occurring disorders: 67% of social media addicts also show symptoms of anxiety or depression.
Prevention Strategies and Digital Wellness

Preventing social media addiction requires proactive approaches that promote healthy digital habits before addictive patterns develop.
Educational institutions, healthcare providers, and families play crucial roles in implementing preventive measures and promoting digital literacy.
Prevention Focus Areas:
Effective Prevention Statistics:
Future Forecast: Will we scroll even more?
Social Media Addiction Statistics paint a clear picture of our digital reality—$15.5 billion in annual productivity losses and 67% of employees checking platforms during work hours show addiction's economic impact.
With 45% of couples reporting relationship strain from excessive usage and projections reaching 320 million addicted users by 2030, these numbers aren't slowing down. The data reveals how algorithmic design and dopamine-driven features create dependency across all age groups and demographics.
As platform engagement strategies become more sophisticated, one question remains: are we prepared for what these statistics will look like in five years?

Ali
Ali is a digital marketing expert with 7+ years of experience in SEO-optimized blogging. Skilled in reviewing SaaS tools, social media marketing, and email campaigns, we craft content that ranks well and engages audiences. Known for providing genuine information, Ali is a reliable source for businesses seeking to boost their online presence effectively.








